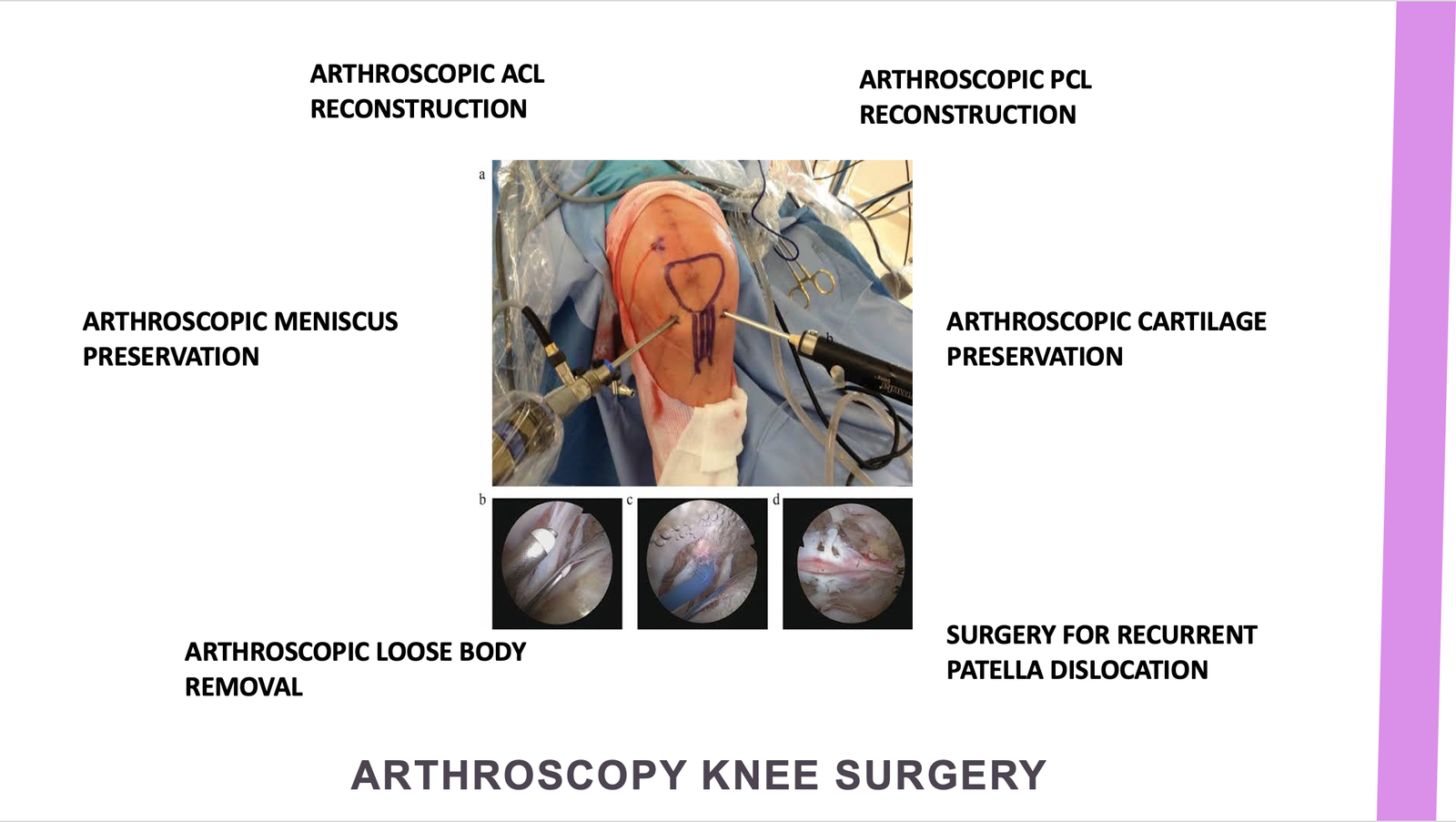
Knee arthroscopy, a commonly performed minimally invasive knee surgery, involves the surgeon creating tiny portals (keyholes) on each side of the kneecap. Through these portals, an arthroscope (small telescope) with an attached video camera is inserted, allowing visualization of the knee joint. Specialized instruments are then utilized through the alternate portal as needed. The images captured by the arthroscope are displayed on a large screen monitor, aiding the surgeon in diagnosing and treating various knee issues with precision. Additionally, images and videos of the knee pathology and surgical procedure can be recorded for further analysis and patient education. Most patients are discharged from the hospital either on the same day of surgery or the following day.
With 7+ years of surgical experience, Dr. Niraj Ranjan Srivastava has undergone extensive and specialized training in arthroscopic knee surgeries across multiple renowned centers in India and UK. He prefers conducting arthroscopic knee surgeries in hospitals equipped with advanced specialized equipment and trained support staff, ensuring optimal outcomes for his patients.
Knee arthroscopy, being minimally invasive, presents numerous benefits:
 Smaller, cosmetically pleasing scars
Smaller, cosmetically pleasing scars
 Reduced tissue damage
Reduced tissue damage
 Minimal discomfort
Minimal discomfort
 Shorter hospital stay (daycare or 1-day admission)
Shorter hospital stay (daycare or 1-day admission)
 Speedier recovery
Speedier recovery
The knee joint is susceptible to a range of injuries and non-traumatic conditions. Common issues where knee arthroscopy might be recommended for diagnosis and treatment include:
 Meniscal tears
Meniscal tears
 Damage to cruciate ligaments such as ACL & PCL
Damage to cruciate ligaments such as ACL & PCL
 Various articular cartilage lesions
Various articular cartilage lesions
 Inflammation of synovial tissue and associated lesions
Inflammation of synovial tissue and associated lesions
 Patellar malalignment
Patellar malalignment
 Baker's cyst: a fluid-filled cyst that forms at the back of the knee due to synovial fluid accumulation. While surgery is often unnecessary, correction of the underlying issue causing fluid buildup is crucial.
Baker's cyst: a fluid-filled cyst that forms at the back of the knee due to synovial fluid accumulation. While surgery is often unnecessary, correction of the underlying issue causing fluid buildup is crucial.
 Specific knee bone fractures like ACL avulsions, intra-articular fractures of the tibia or femur
Specific knee bone fractures like ACL avulsions, intra-articular fractures of the tibia or femur
The steps involved in knee arthroscopy are as follows:
 The procedure is performed on a patient who has been appropriately counseled and has given consent.
The procedure is performed on a patient who has been appropriately counseled and has given consent.
 Knee arthroscopy is conducted under either spinal or general anesthesia, with the method chosen based on the patient's age and health condition.
Knee arthroscopy is conducted under either spinal or general anesthesia, with the method chosen based on the patient's age and health condition.
 The surgeon makes two (occasionally three) small incisions, typically about 5mm in size, around the knee on either side of the patella (kneecap).
The surgeon makes two (occasionally three) small incisions, typically about 5mm in size, around the knee on either side of the patella (kneecap).
 A sterile fluid solution is injected into the knee joint to distend it, creating space and providing a clear view of the internal structures.
A sterile fluid solution is injected into the knee joint to distend it, creating space and providing a clear view of the internal structures.
 An arthroscope, a narrow telescope with a tiny video camera at its end, is inserted through one of the incisions to visualize the knee joint. The images captured are displayed on a large monitor in the operating room.
An arthroscope, a narrow telescope with a tiny video camera at its end, is inserted through one of the incisions to visualize the knee joint. The images captured are displayed on a large monitor in the operating room.
 The surgeon examines the structures inside the knee joint to identify the underlying issue and may take detailed photo images for reference.
The surgeon examines the structures inside the knee joint to identify the underlying issue and may take detailed photo images for reference.
 Once a diagnosis is made or confirmed, surgical instruments such as scissors, motorized shavers, or radiofrequency probes are inserted through another incision to perform the necessary procedures.
Once a diagnosis is made or confirmed, surgical instruments such as scissors, motorized shavers, or radiofrequency probes are inserted through another incision to perform the necessary procedures.
Possible arthroscopic procedures include:
 Repair or removal of a torn meniscus
Repair or removal of a torn meniscus Reconstruction of a torn cruciate ligament (ACL or PCL)
Reconstruction of a torn cruciate ligament (ACL or PCL) Removal of small torn pieces of articular cartilage
Removal of small torn pieces of articular cartilage Removal of loose bone fragments or other debris
Removal of loose bone fragments or other debris Synovectomy to remove inflamed synovial tissue
Synovectomy to remove inflamed synovial tissue Realignment of the patella or lateral release for patellar malalignment
Realignment of the patella or lateral release for patellar malalignment Microfractures to stimulate cartilage regrowth in damaged areas
Microfractures to stimulate cartilage regrowth in damaged areas After completing the arthroscopic procedures, the knee joint is carefully examined for any bleeding or damage. The joint is irrigated with saline solution to clear debris, and excess fluid is drained.
After completing the arthroscopic procedures, the knee joint is carefully examined for any bleeding or damage. The joint is irrigated with saline solution to clear debris, and excess fluid is drained. If bleeding is anticipated, a suction drain may be inserted and removed after 24 hours.
If bleeding is anticipated, a suction drain may be inserted and removed after 24 hours. Finally, the incisions are closed with sutures or adhesive tapes, covered with sterile dressings, and wrapped with compression bandages.
Finally, the incisions are closed with sutures or adhesive tapes, covered with sterile dressings, and wrapped with compression bandages. The patient is then moved to the recovery room for observation.
The patient is then moved to the recovery room for observation.Most patients are discharged either on the same day or the day after knee arthroscopy. Recovery duration varies based on the complexity of the procedure. Simple procedures often lead to faster recovery, typically within 2 to 6 weeks, while complex procedures may necessitate 6 to 12 weeks for full recovery.
Compared to open knee surgery, knee arthroscopy generally involves a quicker recovery.
Pain medication is prescribed for the initial 3 to 5 days post-surgery and is continued as needed thereafter.
Ice packs are applied 4 to 5 times a day for 1 to 2 weeks to help manage swelling.
Before discharge, patients receive instruction from a physiotherapist on knee exercises to be continued at home for 2 to 4 weeks. For complex surgeries, patients may require regular physiotherapy sessions over a longer period, typically 2 to 3 months, to ensure optimal recovery.
While crutches may not always be necessary, they might be required for complex surgeries. Patients undergoing simpler procedures can often begin full weight-bearing immediately after surgery, while others may need to adhere to non-weight-bearing or partial weight-bearing protocols to protect tissues and facilitate healing.
Knee arthroscopy is generally considered a safe procedure, with complications being rare. Potential complications include bleeding into the knee joint, infection, swelling, knee stiffness, blood clots, and damage to surrounding structures such as nerves, blood vessels, joint cartilage, meniscus, and ligaments. Additionally, there may be ongoing knee issues following the surgery.
Address
8/92, Sector 8, Ismailganj, Indira Nagar, Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh 226016
Monday to Friday
10am - 8pm
Appoinments
+91 - 8840223370